函数调用(Function Calling)。简单说,就是你告诉ChatGPT可以用哪些函数,ChatGPT在需要的时候会主动请求你帮它调用这些函数,然后你再把结果告诉它,最终它再给你个完整的回复。
函数调用的两种模式
OpenAI函数调用目前支持两种模式:
- functions 模式(早期版本,比较简单)
- tools 模式(新版本,兼容多种工具类型,OpenAI官方推荐)
我会分别讲一下两种模式怎么用,最后再告诉你实际开发用哪个更好。
第一种模式:functions 模式
functions模式非常直接,你需要定义函数名、函数描述和参数结构。例如,我们想做个查询天气的函数,定义长这样:
"functions": [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
]然后你告诉ChatGPT:“帮我查下北京的天气”,它可能返回:
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"function_call": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\": \"北京\"}"
}
}请求示例:
curl --location 'https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer sk-123123' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "帮我查下北京的天气"
}
],
"functions": [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如 北京"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
},
{
"name": "get_time_info",
"description": "返回今天或指定日期的时间信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date",
"description": "指定的日期,格式为 yyyy-MM-dd,可为空"
}
},
"required": []
}
}
],
"function_call": "auto"
}'
你收到后,就去调用自己的API或者模拟一个结果,再回传给ChatGPT:
- 组装函数调用的消息体
- 组装函数结果的消息体
完整的请求参数示例:
{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "帮我查下北京的天气"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"function_call": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\":\"北京\"}"
}
},
{
"role": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"content": "{ \"city\": \"北京\", \"temperature\": \"23°C\", \"weather\": \"晴转多云\", \"wind\": \"东风 2级\" }"
}
],
"functions": [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如 北京"
}
},
"required": [
"city"
]
}
},
{
"name": "get_time_info",
"description": "返回今天或指定日期的时间信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date",
"description": "指定的日期,格式为 yyyy-MM-dd,可为空"
}
},
"required": [
]
}
}
],
"function_call": "auto"
}ChatGPT最后给你个完整回复:
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "今天北京的天气是晴转多云,气温为23°C,风速为东风2级。",
"refusal": null
},
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}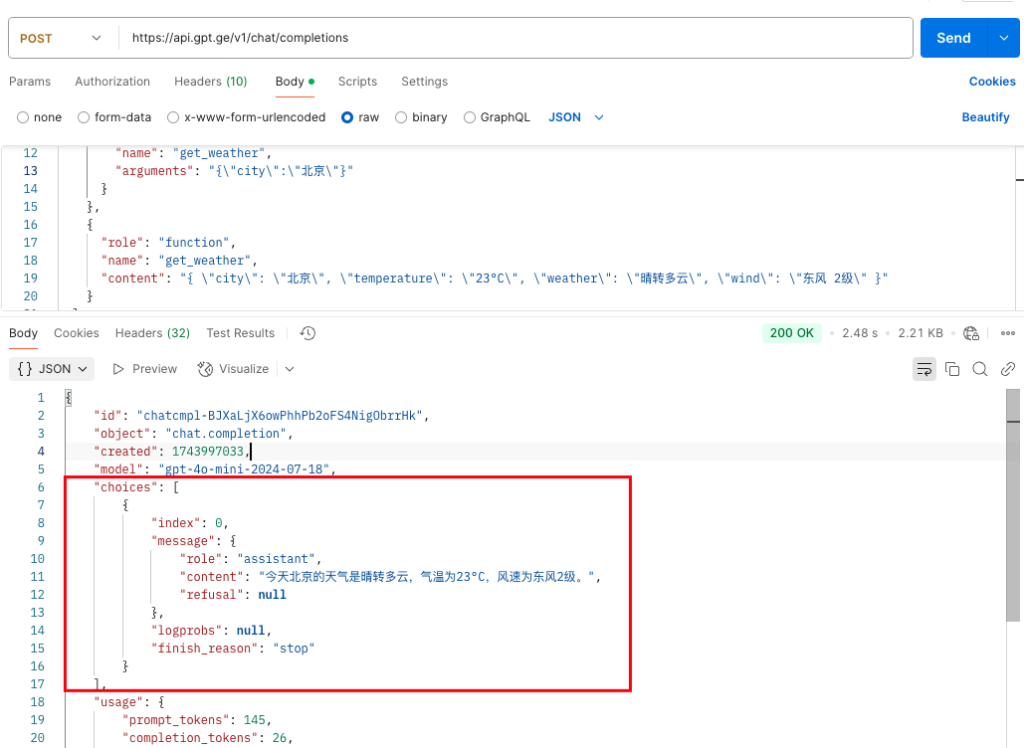
以上:整个函数到函数调用的流程示例
第二种模式:tools 模式
tools模式是OpenAI新版接口,除了函数调用外,还支持Open AI内置工具(code_interpreter, retrieval等)。但实际开发中最常用的还是function功能:
定义tools模式的结构如下:
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto"和functions模式类似,ChatGPT返回时多了个tool_calls字段:
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\": \"上海\"}"
}
}
]
}接下来给它回传结果时,也稍有区别:
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": "call_123",
"name": "get_weather",
"content": "{ \"city\": \"上海\", \"temperature\": \"20°C\", \"weather\": \"阴\", \"wind\": \"北风3级\" }"
}完整的请求参数示例:
{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "帮我查下北京的天气"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "tool_call_1",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\":\"北京\"}"
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": "tool_call_1",
"name": "get_weather",
"content": "{ \"city\": \"北京\", \"temperature\": \"23°C\", \"weather\": \"晴转多云\", \"wind\": \"东风 2级\" }"
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如 北京"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_time_info",
"description": "返回今天或指定日期的时间信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date",
"description": "指定的日期,格式为 yyyy-MM-dd,可为空"
}
},
"required": []
}
}
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto"
}返回结果示例:
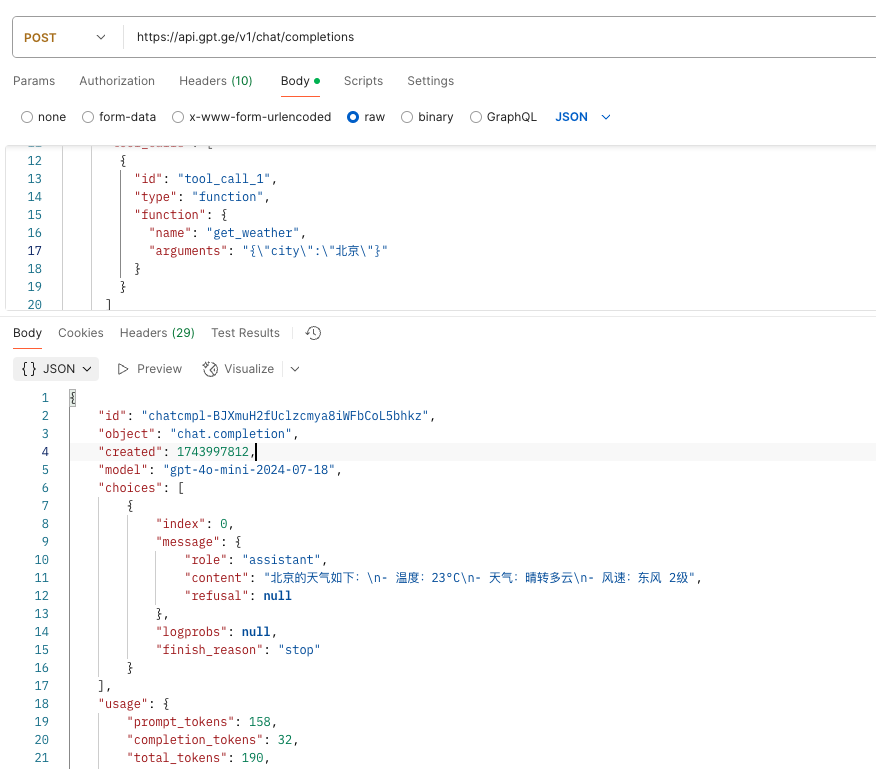
哪个模式更好用?
- 如果你只关心函数调用,两个都可以用。但OpenAI官方推荐未来使用tools模式。
- 如果你打算使用更多OpenAI平台功能(如代码解释器、文档搜索),则一定要用tools模式。
- 如果你用的是开源模型(如Ollama的模型),建议只使用tools中的
function类型,其他类型没法支持。
个人建议新项目统一使用tools模式,方便未来扩展,也兼容大多数开源模型。
函数/工具描述是否算入TOKEN ?
结论:是的
原理:
函数定义的结构,比如下面这段内容👇,每个字段都是 token:
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "根据城市名称查询当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如 Beijing"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
OpenAI 会先把这个解释给模型,就像是说:
“你现在有一个函数叫 get_weather,它接收参数 city,功能是查天气”。
🧮 举个例子:实际 token 计算
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 102,
"completion_tokens": 15,
"total_tokens": 117,
"prompt_tokens_details": {
"cached_tokens": 0,
"audio_tokens": 0
},
"completion_tokens_details": {
"reasoning_tokens": 0,
"audio_tokens": 0,
"accepted_prediction_tokens": 0,
"rejected_prediction_tokens": 0
}
}这个 102 中就包含了你输入的 user prompt + 所有 functions 定义的 token。
如果定义多个函数或者函数结构很复杂,那 prompt_tokens 会更高。
🚀 如何优化?
如果在大量调用时有成本考虑,可以考虑以下方式优化 token 消耗:
1. 减少函数数量:只传需要的函数,而不是每次都传所有函数。
2. 简化函数描述:description 字段简洁明了就行,别啰嗦。
3. 控制参数结构深度:别用太复杂的嵌套 object,模型理解能力已经够强,能推断不少。
以下是一些参考资料: